 Earlier this week, the Supreme Court handed down its decision in Fourth Estate v. Wall-Street.com, a case examining the registration precondition to filing a suit for copyright infringement in the federal district courts. While I agree with the Court’s exegesis of the statute at issue, it’s worth noting how the Court’s construction leaves many, if not most, copyright owners in the lurch. Under the Court’s holding, in fact, this very blog post could be infringed today, and there’s very little that could be done to stop it for many months to come. As the Court noted in Harper & Row v. Nation, “copyright supplies the economic incentive to create and disseminate ideas.” The Court’s holding in Fourth Estate, by contrast, disincentivizes dissemination since it undermines effective copyright protection and prejudices the public interest in the production of, and access to, creative works. Again, I don’t blame the Court for this outcome—in fact, I think it’s correct. The problem, as I’ll explain, lies in the unfortunate fact that nowadays it takes too long to register a copyright claim. And that’s something that Congress needs to fix.
Earlier this week, the Supreme Court handed down its decision in Fourth Estate v. Wall-Street.com, a case examining the registration precondition to filing a suit for copyright infringement in the federal district courts. While I agree with the Court’s exegesis of the statute at issue, it’s worth noting how the Court’s construction leaves many, if not most, copyright owners in the lurch. Under the Court’s holding, in fact, this very blog post could be infringed today, and there’s very little that could be done to stop it for many months to come. As the Court noted in Harper & Row v. Nation, “copyright supplies the economic incentive to create and disseminate ideas.” The Court’s holding in Fourth Estate, by contrast, disincentivizes dissemination since it undermines effective copyright protection and prejudices the public interest in the production of, and access to, creative works. Again, I don’t blame the Court for this outcome—in fact, I think it’s correct. The problem, as I’ll explain, lies in the unfortunate fact that nowadays it takes too long to register a copyright claim. And that’s something that Congress needs to fix.
The issue in Fourth Estate is straightforward. Under the first sentence of Section 411(a) of the Copyright Act, “no civil action for infringement of the copyright in any United States work shall be instituted until preregistration or registration of the copyright claim has been made in accordance with this title.” Some courts, like the Ninth Circuit, have applied the so-called “application approach,” finding that “registration . . . has been made” when the copyright owner delivers a complete application to the Copyright Office. Other courts, like the Tenth Circuit, have applied the so-called “registration approach,” where “registration” is not “made” until the Register of Copyrights has acted upon the application (by either approving or rejecting it). Confounding the analysis is the fact that other sections of the Copyright Act alternatively delineate registration as something done by the applicant or by the Copyright Office.
In the decision below, the Eleventh Circuit applied the registration approach, affirming the district court’s dismissal of Fourth Estate’s complaint since the Register of Copyrights had not yet approved or denied its application to register. The Supreme Court, in a unanimous decision by Justice Ginsburg, affirmed: “We hold . . . that registration occurs, and a copyright claimant may commence an infringement suit, when the Copyright Office registers a copyright.” The issue for the Court was one of pure statutory construction, and the problem for proponents of the application approach is that the second sentence of Section 411(a) clearly indicates that registration is something done by the Copyright Office. It provides, as an exception to the first sentence, that a copyright owner can nevertheless sue for infringement once the application materials “have been delivered to the Copyright Office in proper form and registration has been refused.”
Justice Ginsburg reasoned: “If application alone sufficed to ‘ma[ke]’ registration, § 411(a)’s second sentence—allowing suit upon refusal of registration—would be superfluous.” I’ve always found this to be the better argument, and I’m not surprised to see it front-and-center in the Court’s analysis. Why would applicants need an exception that turns on the subsequent action of the Copyright Office if merely delivering a completed application sufficed? As Justice Ginsburg noted, the application approach “requires the implausible assumption that Congress gave ‘registration’ different meanings in consecutive, related sentences within a single statutory provision.” I think the Court got this one exactly right, and I don’t find arguments to the contrary to be particularly persuasive.
That said, let me now explain why it’s wrong—well, at least why it’s bad for millions of copyright owners and why Congress should fix it ASAP.
The purpose of the registration approach and other similar provisions in the Copyright Act (such as the availability of statutory damages or attorney’s fees) is to incentivize timely registration, which is no longer a prerequisite to copyright protection as it was under the Copyright Act of 1909. Under the current Copyright Act, copyright protection nominally exists once a work is fixed in a tangible medium of expression, and registration is no longer mandatory. (I say “nominally” because the Court’s holding in Fourth Estate ensures that, as a practical matter, countless works with respect to which copyright owners have exclusive rights on paper in fact have no immediate rights in the real world since they can’t actually file suit to quickly stop any ongoing infringement.) However, the incentive-to-register theory makes little sense in the context of the debate over the proper interpretation of Section 411(a) itself as the works being sued upon must be registered under both the application and registration approaches.
With due respect to the Copyright Office, processing a registration application is primarily a ministerial act. The vast majority of applications are granted—97% in 2017 according to the latest available data from the Copyright Office (though 29% of those applications required correspondence with the applicant). Are we really withholding remedies for all copyright owners because of the remaining 3%? And even for the 3% of applications that are denied, the copyright owner can still sue for infringement, asking the district court to reassess the agency’s refusal. No matter what the Copyright Office does with the application, whether it grants or denies, the copyright owner ultimately can sue. And, under the third sentence of Section 411(a), the Register of Copyrights can even “become a party to the action with respect to the issue of registrability of the copyright claim.” So it’s not like the Register can’t have a say should the application be in that slim minority of questionable ones that may merit intervention.
To its credit, the Supreme Court acknowledged that its holding would cause problems for copyright owners—but it also overplayed the exceptions to the registration approach that Congress put in place to alleviate some of these issues. For example, Justice Ginsburg pointed out that Section 408(f) empowers the Register of Copyrights to establish regulations for the preregistration of certain categories of works. Under this regime, as Justice Ginsburg noted, “Congress provided that owners of works especially susceptible to prepublication infringement should be allowed to institute suit before the Register has granted or refused registration.” That’s great for that particular subset of copyright owners, but what about everyone else? And what about authors who publish their works just as soon as they create them? Moreover, Justice Ginsburg’s blithe comment that copyright owners “may eventually recover damages for the past infringement” ignores the fact that injunctive relief to stop the actual, ongoing infringement is unavailable until the registration is processed by the Copyright Office.
The Court laments such policy ramifications: “True, the statutory scheme has not worked as Congress likely envisioned. Registration processing times have increased from one or two weeks in 1956 to many months today.” And this gets to the heart of the problem: The time it takes the Copyright Office to process an application has significantly increased over the years. Just four years after the Copyright Act of 1976 went into effect, the delay was “5 to 6 weeks.” And, as of October 2018, the delay has grown to an “average processing time for all claims” of “7 months.” Indeed, the fastest the Copyright Office processes an application now is one month, and the longest it takes is an incredible 37 months. The following illustration from the Copyright Office breaks this down with more particularity:
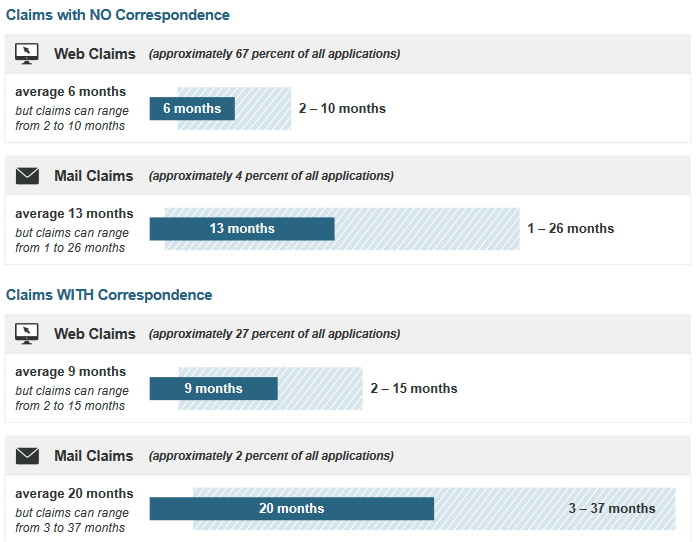
To be clear, I don’t think these delays are the Copyright Office’s fault. In fact, I think it’s Congress’s fault for not giving the agency more resources to do the very things that Congress requires it to do. Regardless, the fact remains that even copyright owners who do everything that the Copyright Act expects them to do in order to obtain the greatest protection for their works at the earliest that they can reasonably do so are still left without remedies should—or, perhaps more likely, when—infringement occur once they release their works to the world. The aforementioned constitutional goal of dissemination is thus undercut by the subservient goal of registration, for rational copyright owners would be less motivated to disseminate their works by the right to exclude when that right is in fact illusory. If Congress really wants authors to promote progress via dissemination of new works, it should adjust Section 411(a) to provide for immediate protection to all works, whether registered or not. It can still incentivize registration by limiting the remedies available, but it shouldn’t make it so that there are none.
To see the injustice, one need look no further than this very blog post. According to the Copyright Act, this post was protected the moment it was fixed in a tangible medium of expression (i.e., yesterday evening). Should the copyright owner—presumably the university where I work as this is a work made for hire—have filed for registration as quickly as possible (i.e., this morning), there still would be no way to obtain any injunctive relief while the Copyright Office processes the application. Preregistration was never an option as this post is not a literary work that is protected by the exception for certain works prone to prepublication infringement under Section 202.16 of the CFR. Even if the university had done everything that it was supposed to do as early as it could reasonably have done so to ensure the utmost copyright protection for this post, it could do nothing in the courts to stop an infringer who willfully exploits this post for profit until the Copyright Office acts upon the application—a lifetime for infringement in the digital age. (There is an option to expedite review for $800, but that amount of money is not reasonable for most people.)
Perhaps a takedown notice could be issued under Section 512 of the DMCA, but if there’s a counternotice, the university could not bring suit in the designated 10-14 day window to prevent the service provider from restoring the infringing material since there’s been no registration and thus it cannot sue for infringement. Despite having done everything Congress expected, the university would be powerless to stop the ongoing infringement of its exclusive rights in this post for perhaps several months into the future. And any argument that damages will compensate for infringements occurring before the Copyright Office got around to acting on the application is undercut by the fact that courts routinely grant preliminary injunctive relief precisely because the harm from infringement is irreparable—money damages cannot make the copyright owner whole.
The absurd result of all this is that the promise of exclusive rights in one’s original work of authorship is practically meaningless given the registration approach under Section 411(a). No doubt, Congress intended this disability to act as a stick in order to encourage the carrot of remedies should those rights be infringed. But the reality is that numerous copyright owners who do everything right get the stick and not the carrot—at least until the Copyright Office happens to process their applications. In the meantime, these copyright owners cannot be faulted for thinking twice before disseminating their works. Since enforcement of their rights is precluded through no fault of their own, what else does Congress expect them to do? A right without a remedy is senseless, and given the millions of original works that are created each day, Congress’s promise of copyright protection for new works may be one of the most illusory rights in modern times. Now that the Supreme Court has clarified Section 411(a), it’s time for Congress to fix it.